Digital Voltmeter Principle
Digital Voltmeter Definition
A digital voltmeter is an electronic device that measures voltage by converting the analog signal into digital data and displaying it numerically.

Working Principle
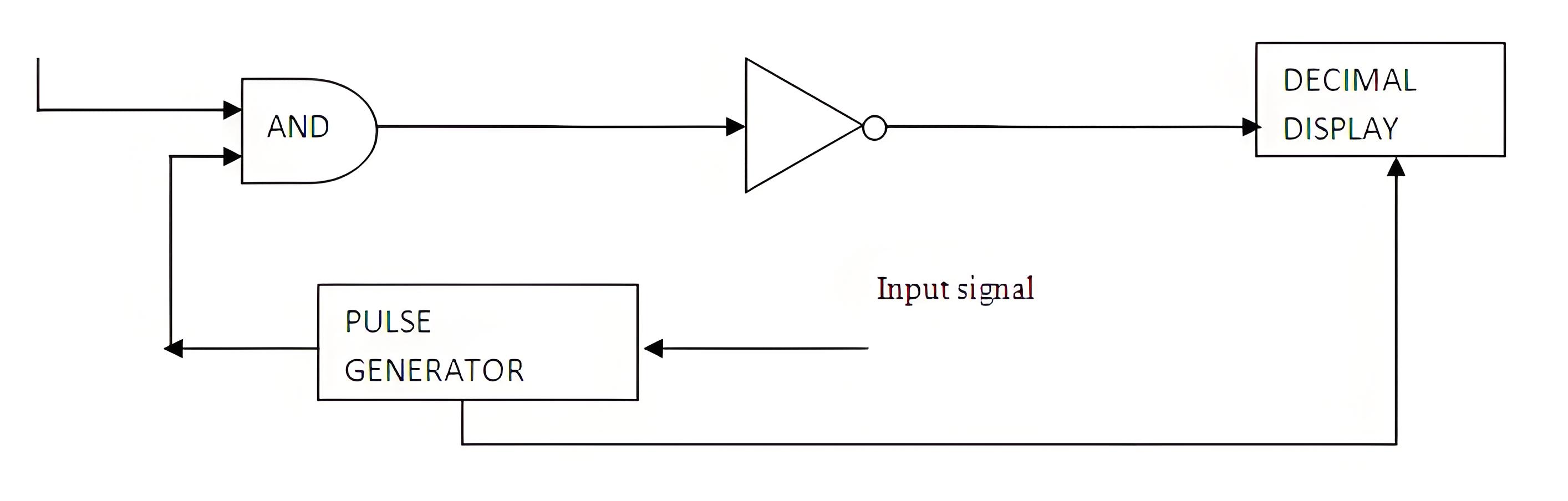
The block diagram of a simple digital voltmeter is shown in the figure.
Input Signal: This is the voltage that needs to be measured.
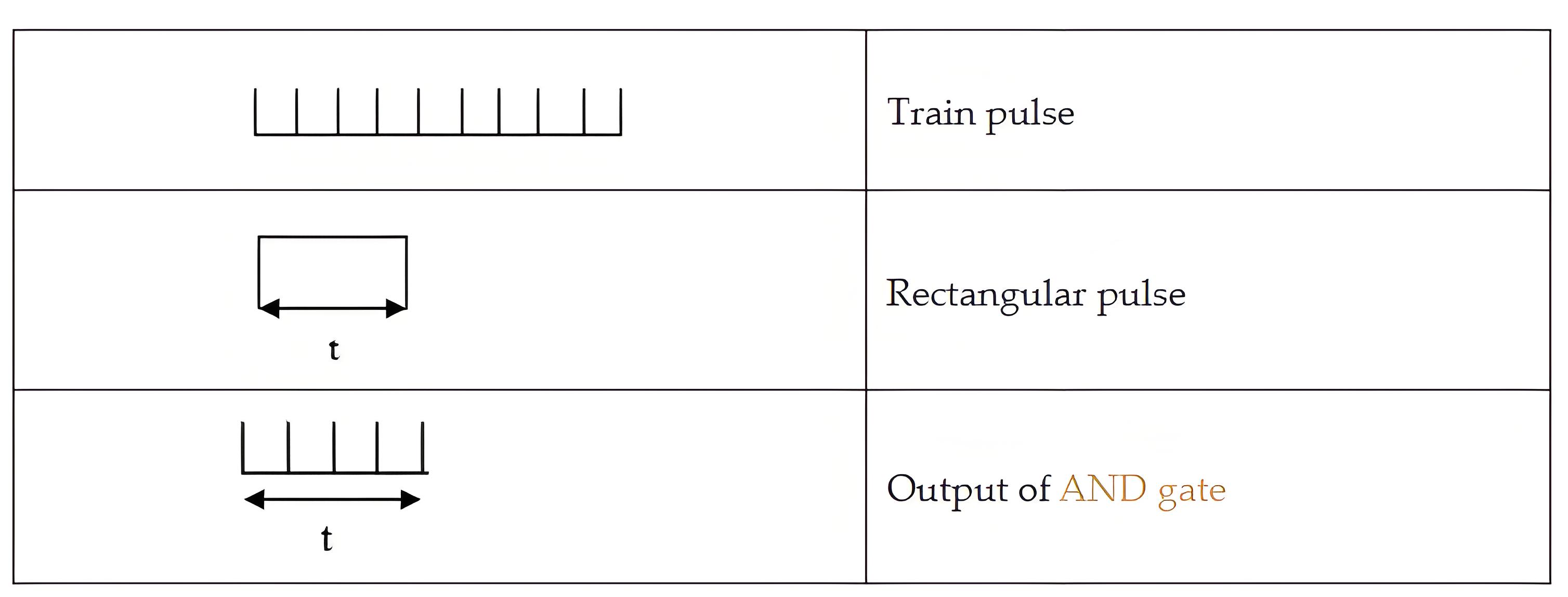
Pulse generator: Actually it is a voltage source. It uses digital, analog or both techniques to generate a rectangular pulse. The width and frequency of the rectangular pulse is controlled by the digital circuitry inside the generator while amplitude and rise and fall time is controlled by analog circuitry.
AND Gate: This gate outputs a high signal only when both of its inputs are high. Combining a train pulse with a rectangular pulse, it outputs train pulses that match the duration of the rectangular pulses generated.
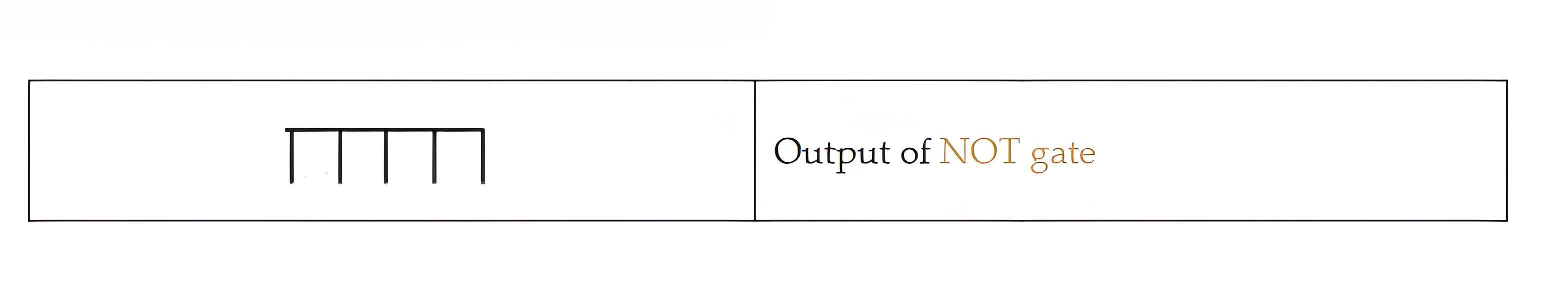
NOT gate: It inverts the output of AND gate.
Types of Digital Voltmeters
Ramp type digital voltmeter
Integrating type voltmeter
Potentiometric type digital voltmeters
Successive approximation type digital voltmeter
Continuous balance type digital voltmeter
Advantages Associated with Digital Voltmeters
Readout of DVMs is easy as it eliminates observational errors in measurement committed by operators.
Error on account of parallax and approximation is entirely eliminated.
Readings are obtained quickly, enhancing efficiency.
Output can be fed to memory devices for storage and future computations.
Versatile and accurate
Compact and cheap
Low power requirements
Portability increased
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













