What is an Electronic DC Voltmeter?
What is an Electronic DC Voltmeter?
Electronic DC Voltmeter Definition
An electronic DC voltmeter is defined as a device that measures direct current (DC) voltage across any two points in an electric circuit using semiconductor components.
DC Voltage
DC voltage is a constant voltage from sources like batteries and solar cells, with no change in polarity or magnitude over time.
Working Principle
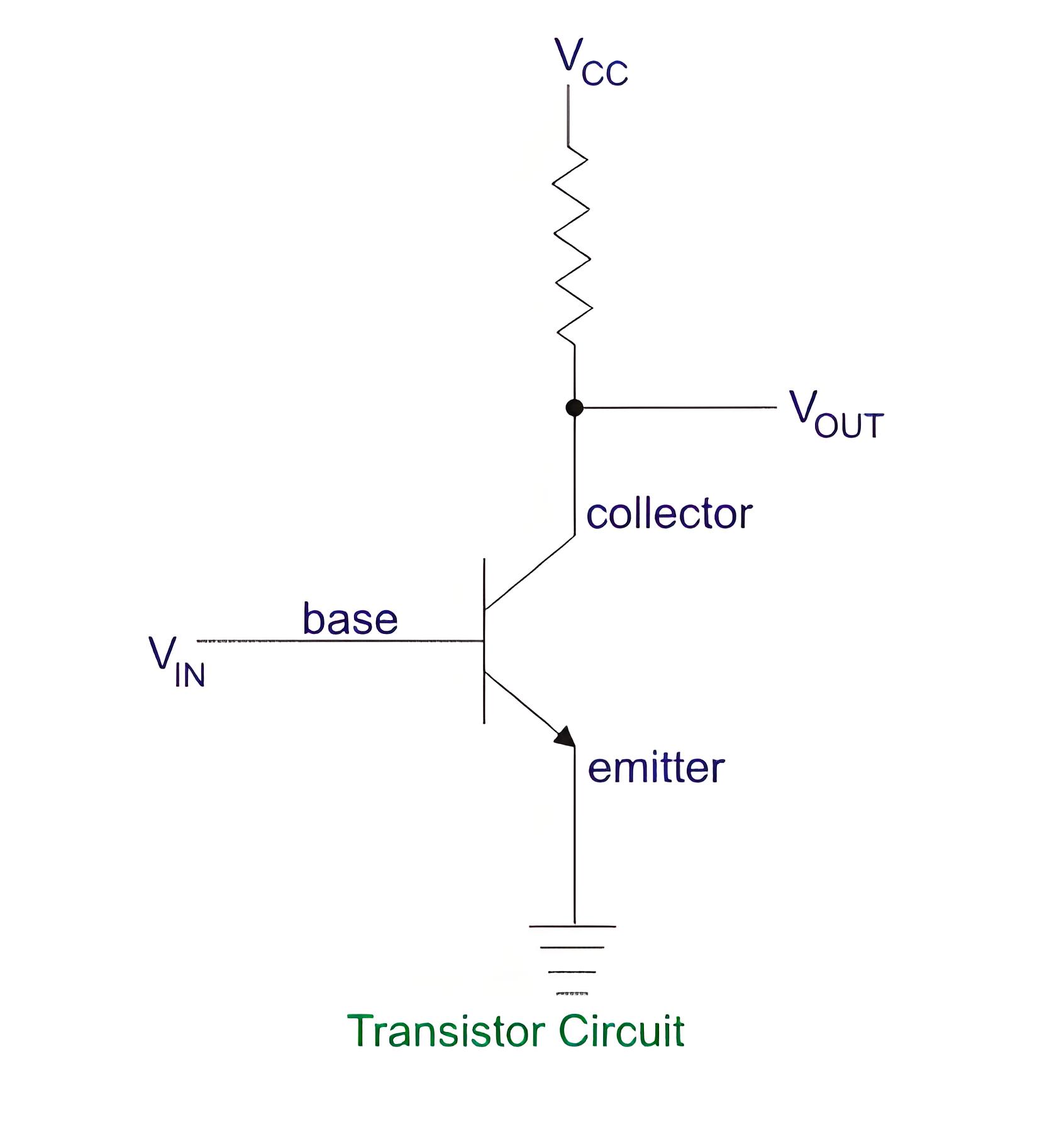
Electronic DC voltmeters convert DC voltage to a proportional current displayed by a meter, using components like resistors and amplifiers.
The main components of an electronic DC voltmeter are:
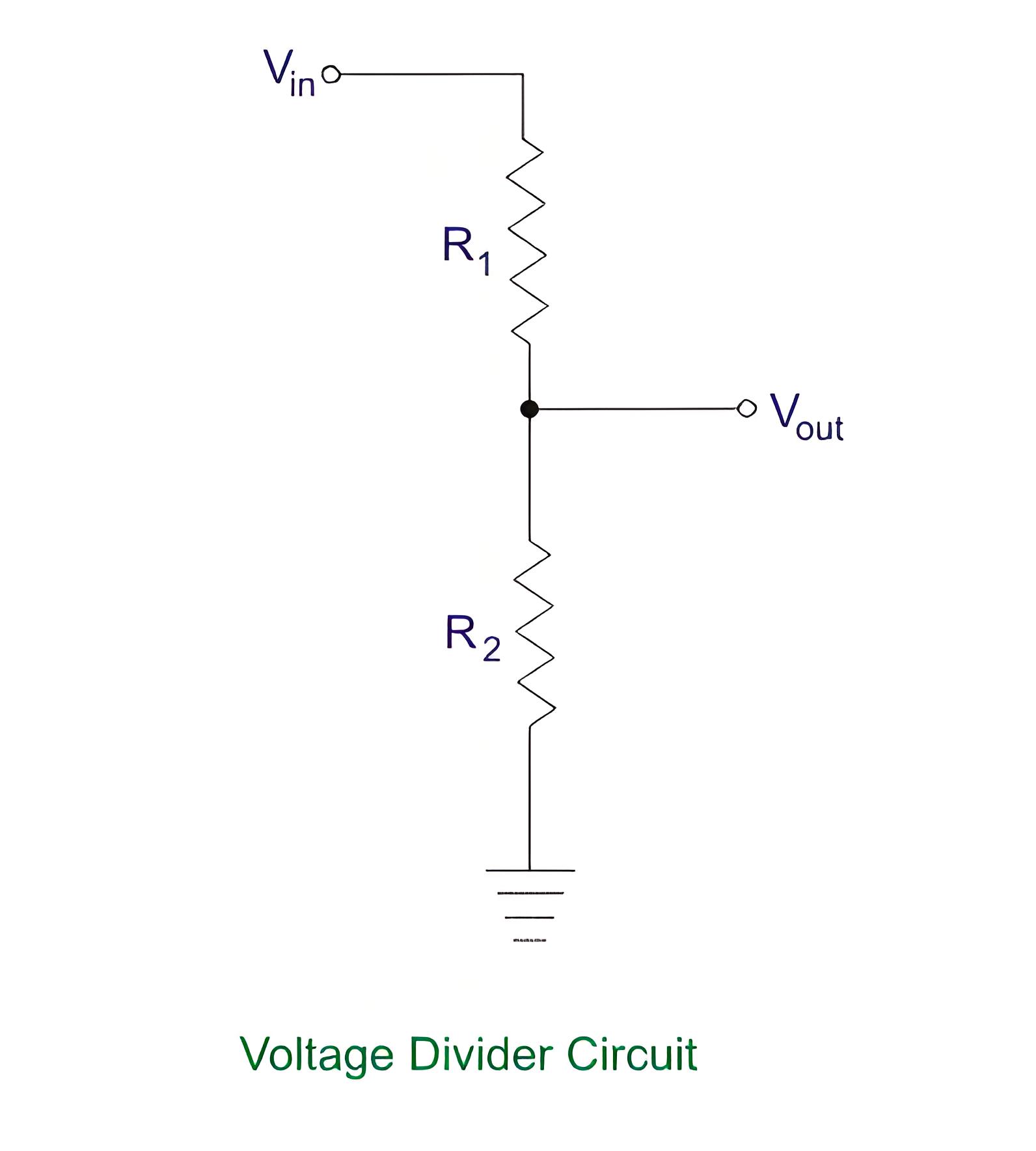
Voltage divider: This is a series of resistors that divides the input voltage into smaller voltage that can be applied to the meter movement. The value of the resistors determines the range and sensitivity of the voltmeter. The voltage divider also provides isolation and protection for the meter movement from high voltages.
Types of Electronic DC Voltmeters
There are various types of electronic DC voltmeters, each with different designs and functions. Common types include:
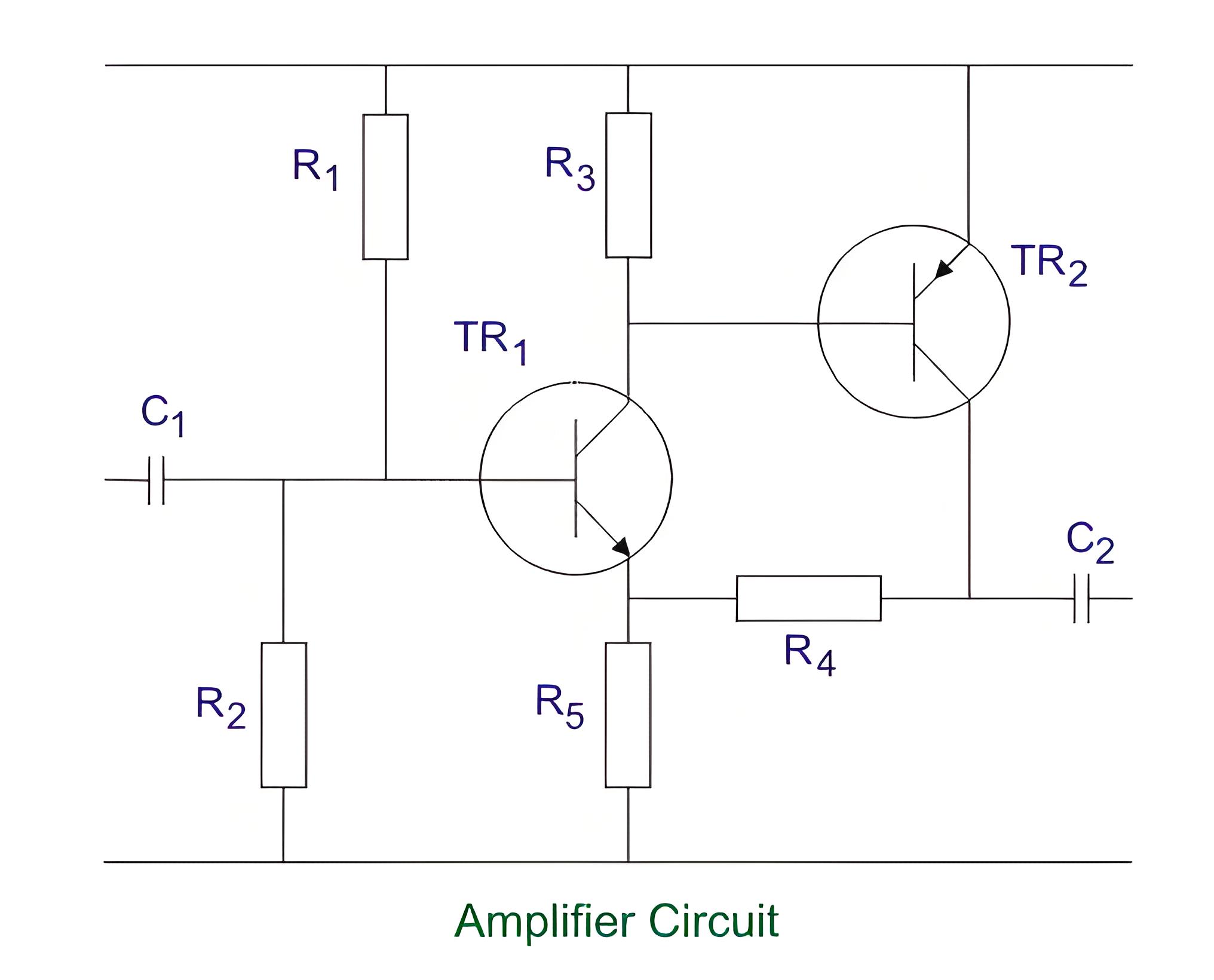
Average reading diode vacuum tube voltmeter: This type of voltmeter uses a vacuum tube diode to rectify the AC voltage into a pulsating DC voltage. The average value of this voltage is measured by a PMMC galvanometer. This type of voltmeter has a simple construction, high input resistance, and low power consumption. However, it has low bandwidth, non-linear operation, and poor accuracy when measuring low voltages.
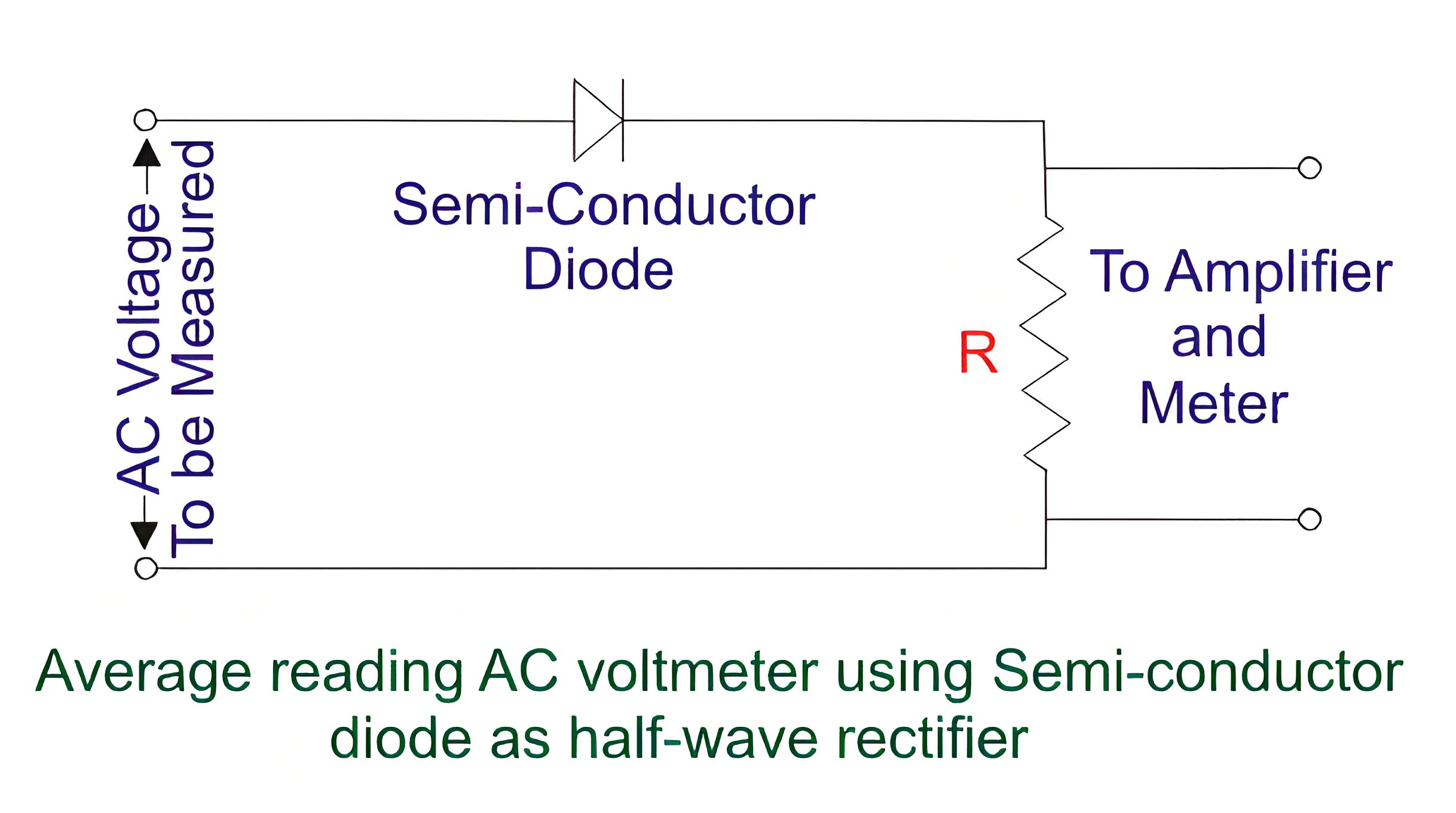
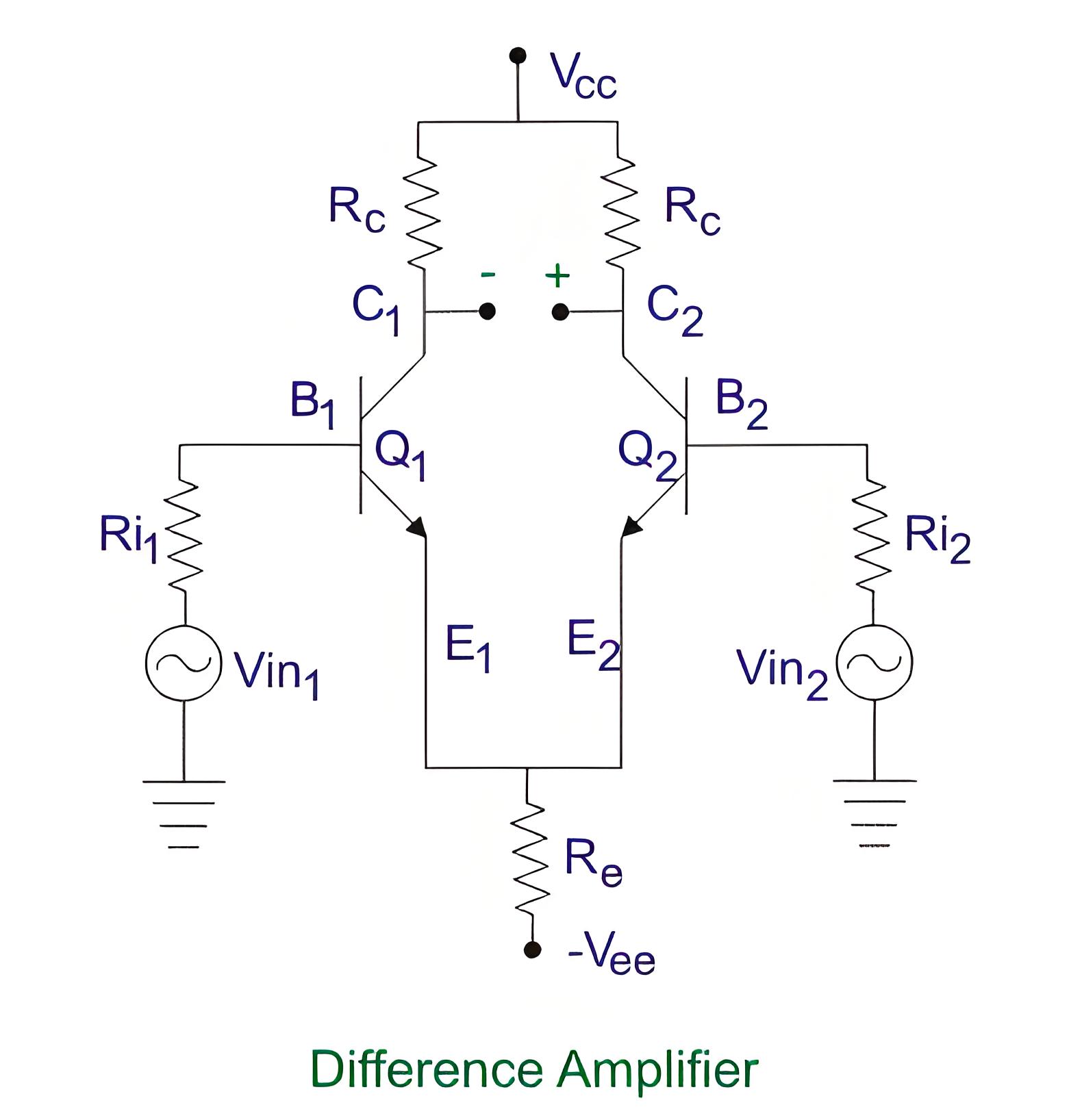
Applications of Electronic DC Voltmeters
Electronic DC voltmeters are widely used in various fields of science, engineering, and technology for measuring DC voltages. Some of the applications are:
Testing and troubleshooting electronic circuits and devices
Measuring battery voltages and charging levels
Measuring solar panel voltages and power outputs
Measuring sensor outputs and signal levels
Measuring electrostatic potentials and fields
Measuring bioelectric potentials and signals
Conclusion
An electronic DC voltmeter is defined as a device that measures the direct current (DC) voltage across any two points in an electric circuit. It uses semiconductor components like diodes, transistors, and amplifiers for better sensitivity and accuracy. Types include average reading diode vacuum tube voltmeters, peak reading diode vacuum tube voltmeters, difference amplifier voltmeters, and digital multimeters. These voltmeters are vital for testing, troubleshooting, and designing electronic circuits, measuring DC voltages from microvolts to kilovolts with high precision and speed. They are essential for electrical and electronic engineers, technicians, and hobbyists.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













