What is a PMMC?
PMMC Meter Definition
A PMMC meter (also known as a D’Arsonval meter or galvanometer) is defined as a device that measures the current through a coil by observing the coil’s angular deflection in a uniform magnetic field.
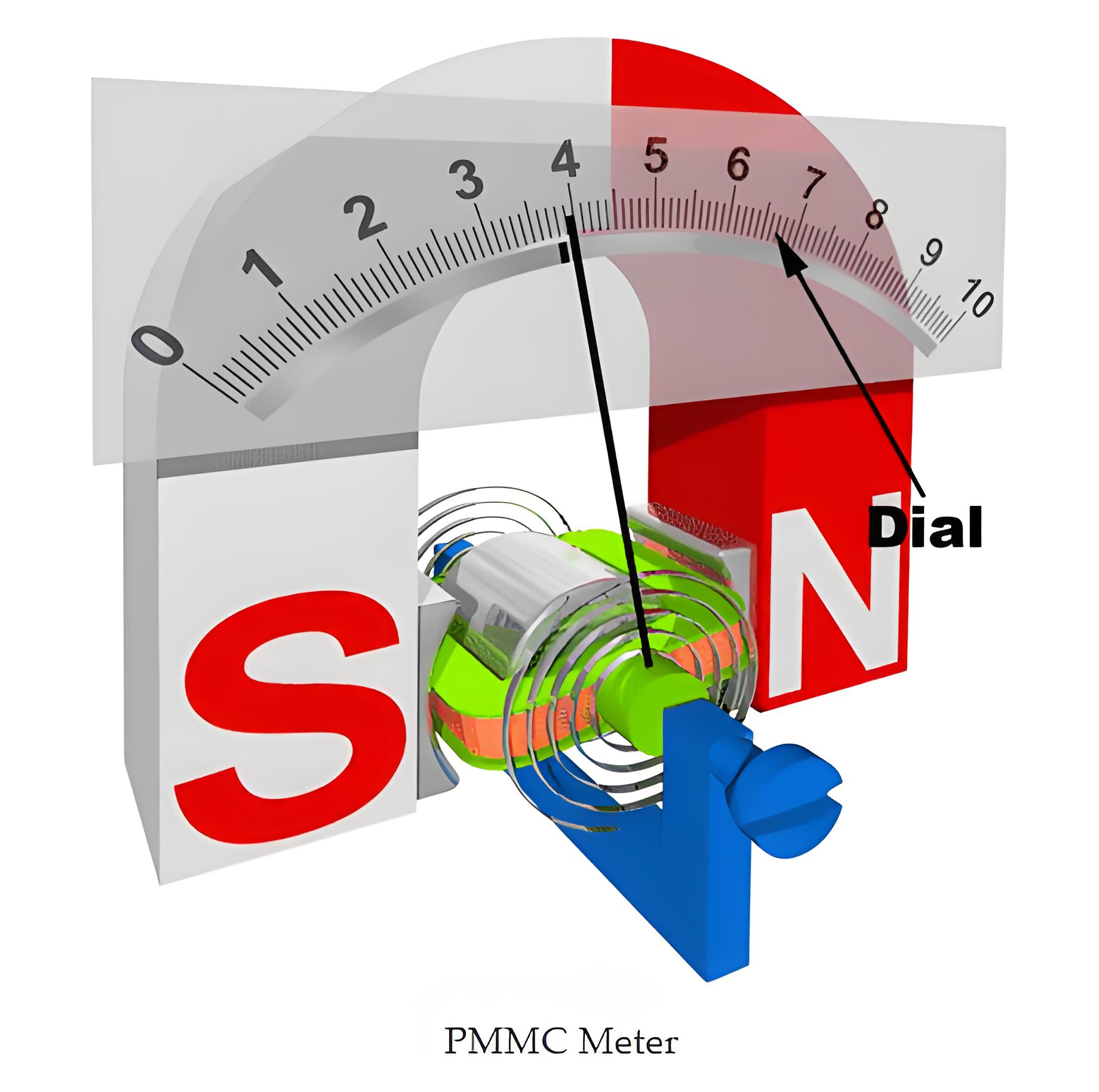
PMMC Construction
A PMMC meter (or D’Arsonval meters) is constructed of 5 main components:
Stationary Part or Magnet System
Moving Coil
Control System
Damping System
Meter
Working Principle
A PMMC meter uses Faraday’s Laws of electromagnetic induction, where a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field experiences a force proportional to the current, moving a pointer on a scale.
PMMC Torque Equation
Let us derive a general expression for torque in permanent magnet moving coil instruments or PMMC instruments. We know that in moving coil instruments the deflecting torque is given by the expression:
Td = NBldI where N is number of turns,
B is magnetic flux density in air gap,
l is the length of moving coil,
d is the width of the moving coil,
I is the electric current.
Now for a moving coil instrument the deflecting torque should be proportional to current, mathematically we can write Td = GI. Thus on comparing we say G = NBIdl. At steady state we have both the controlling and deflecting torques are equal. Tc is controlling torque, on equating controlling torque with deflection torque we have ,GI = K.x where x is deflection thus current is given by
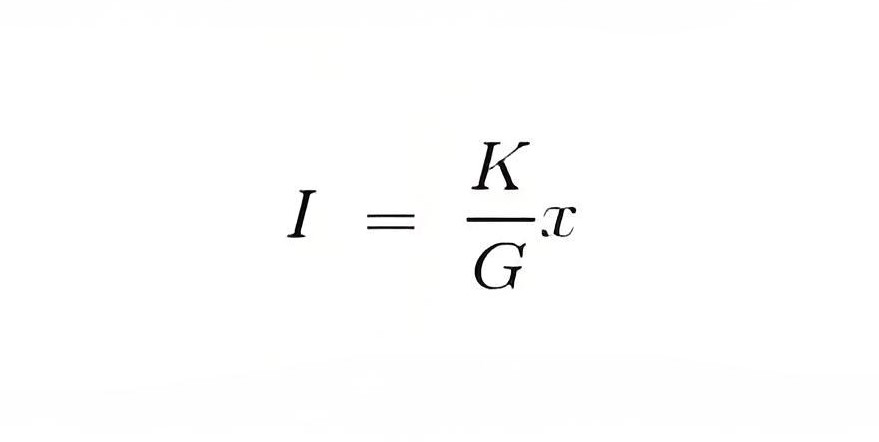
Since the deflection is directly proportional to the current therefore we need a uniform scale on the meter for measurement of current.
Now we are going to discuss about the basic circuit diagram of the ammeter. Let us consider a circuit as shown below:
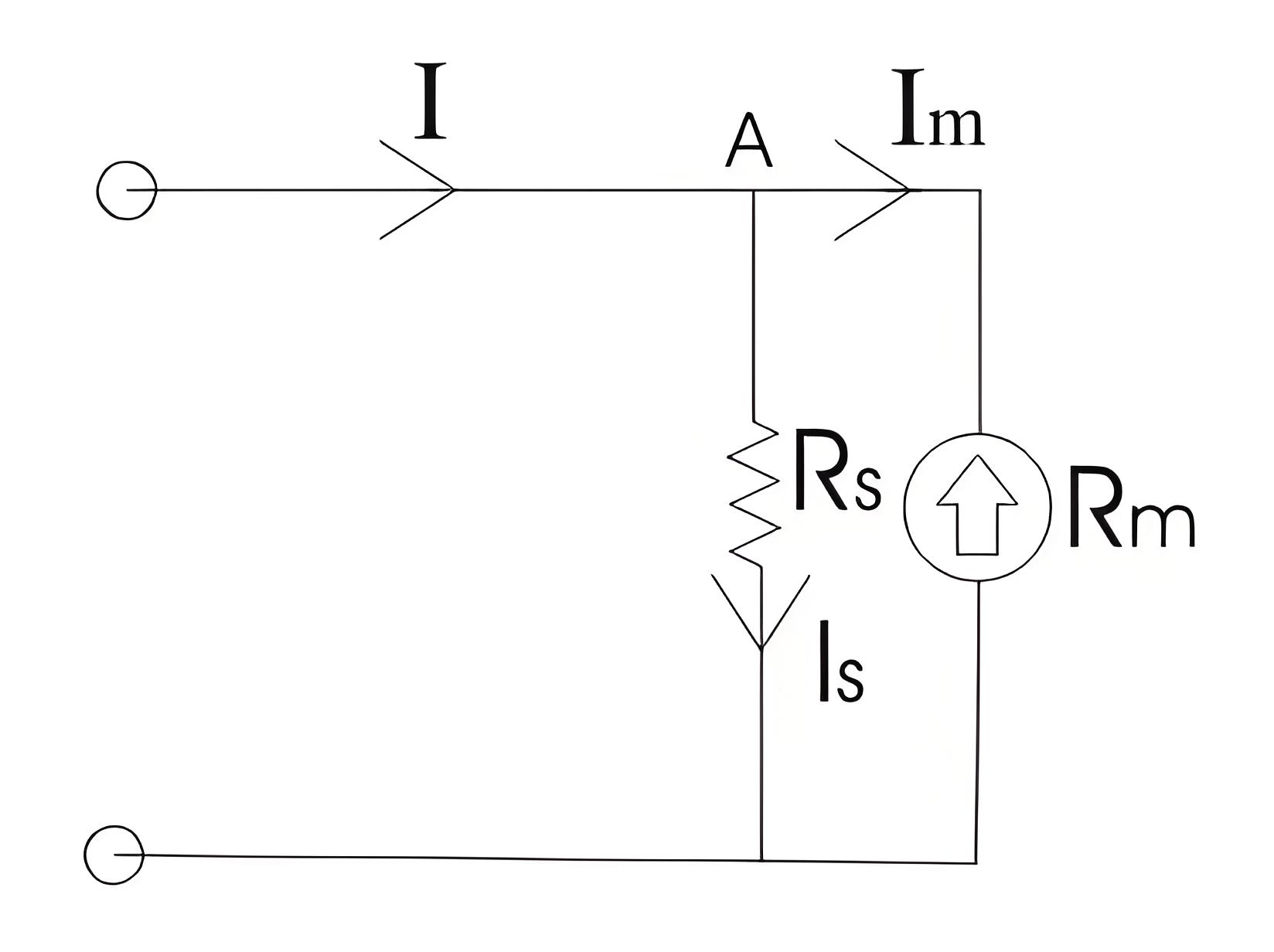
The current I splits into two components at point A: Is and Im. Before discussing their magnitudes, let’s understand shunt resistance construction. The main properties of shunt resistance are detailed below:
The electrical resistance of these shunts should not differ at higher temperature, it they should posses very low value of temperature coefficient. Also the resistance should be time independent. Last and the most important property they should posses is that they should be able to carry high value of current without much rise in temperature. Usually manganin is used for making DC resistance. Thus we can say that the value of Is much greater than the value of Im as resistance of shunt is low. From the we have,
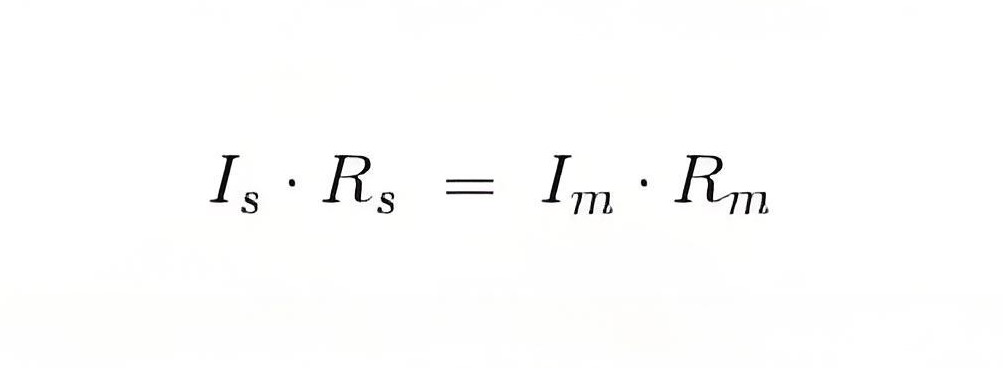
Where, Rs is resistance of shunt and Rm is the electrical resistance of the coil.
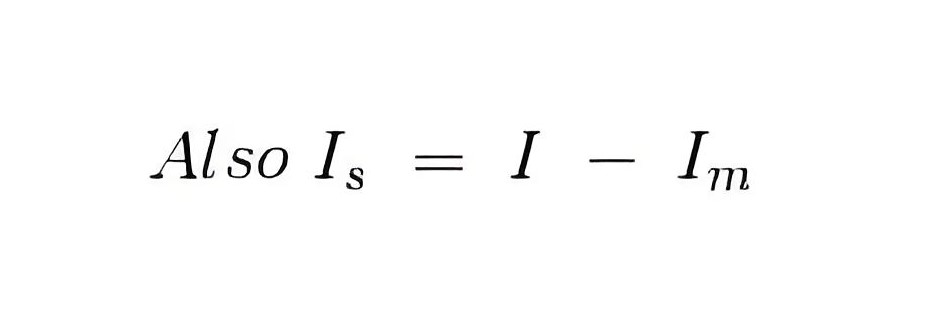
From the above two equations we can write,
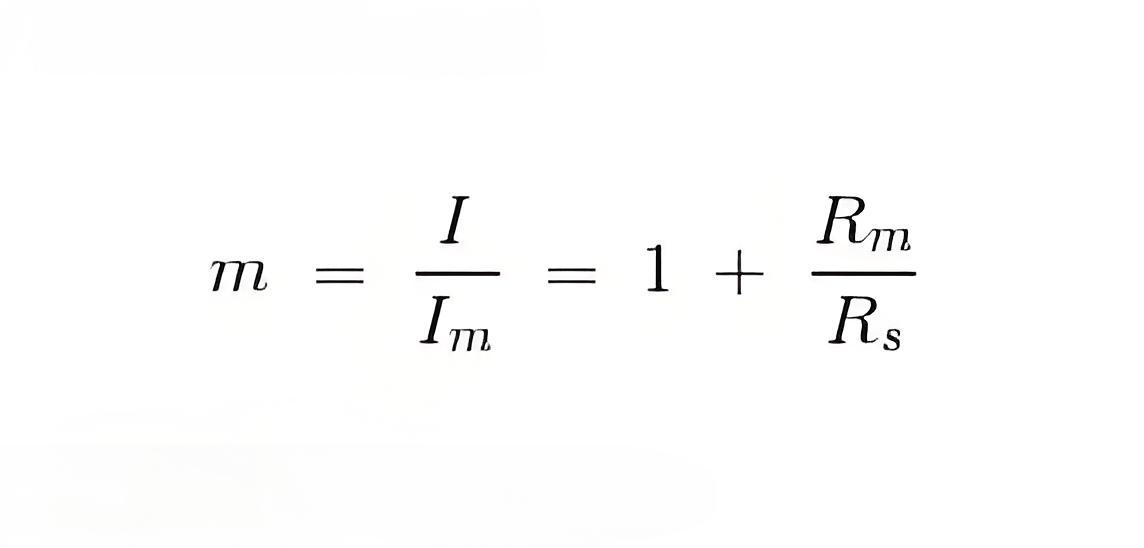
Where, m is the magnifying power of the shunt.
Errors in Permanent Magnet Moving Coil Instruments
Errors due to permanent magnets
Change in the resistance of the moving coil with the temperature
Advantages of Permanent Magnet Moving Coil Instruments
The scale is uniformly divided as the current is directly proportional to deflection of the pointer. Hence it is very easy to measure quantities from these instruments.
Power consumption is also very low in these types of instruments.
A high torque to weight ratio.
These are having multiple advantages, a single instrument can be used for measuring various quantities by using different values of shunts and multipliers.
Disadvantages of Permanent Magnet Moving Coil Instruments
These instruments cannot measure AC quantities.
The cost of these instruments is high as compared to moving iron instruments.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













