What is an Integral Controller?
What is an Integral Controller?
Integral controller definition
Integral controller is another basic control algorithm in automatic control systems, usually represented by the letter "I". The integral controller adjusts the output of the controller by accumulating error signals to eliminate steady-state errors in the system.
Basic principle
The basic idea of the integral controller is to accumulate error signals during the control process and use the accumulated results to adjust the output of the controller.
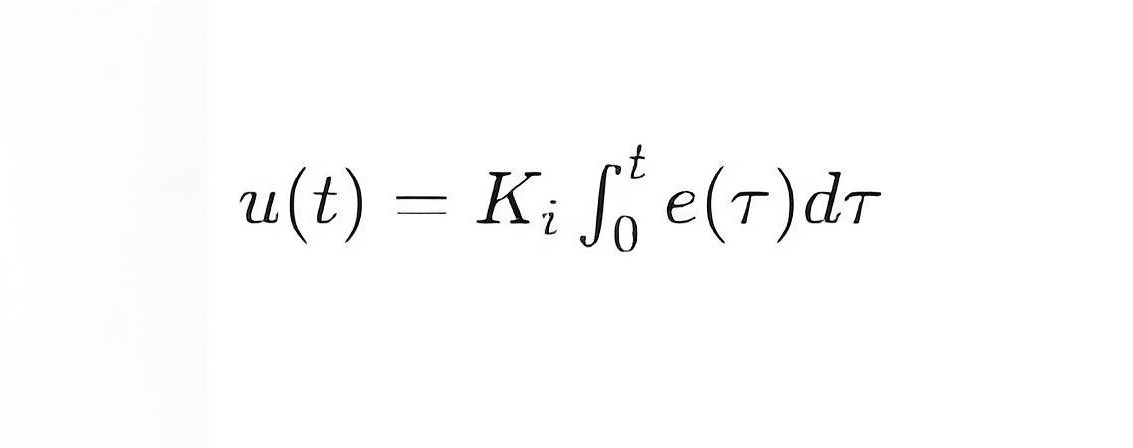
u(t) is the output signal of the controller.
Ki is an Integral Gain, which determines the amplification of the output signal to the accumulation of errors.
e(t) is the error signal, defined as e(t)=r(t)−y(t), where r(t) is the set value and y(t) is the actual measured value.
Controller output
The output of the integration controller can be expressed as:
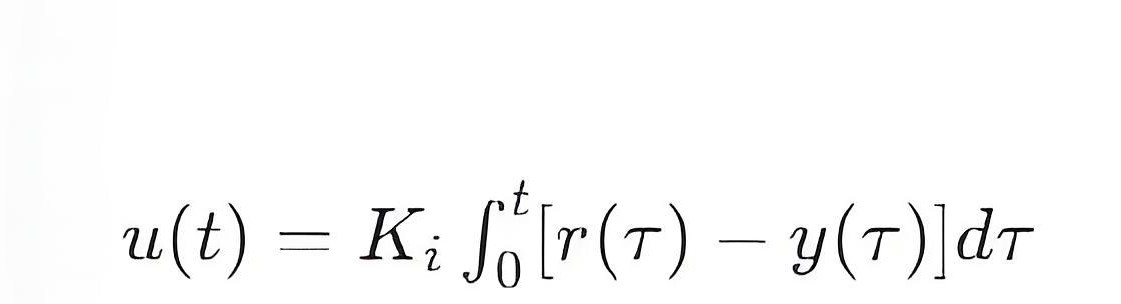
Ki here is a constant that can be adjusted to change the speed and strength of the controller's response to the accumulation of errors.
Advantage
Eliminate steady-state error: The integral controller can eliminate steady-state error in the system, so that the system is finally stable at the set value.
Improve accuracy: By accumulating error signals, the control accuracy of the system can be improved.
Shortcoming
Slow response: Due to the need to accumulate error signals, the response speed of the integral controller is slow.
Overtuning: If the integration gain is not selected properly, it may lead to overtuning of the system.
Stability issues: Integral controllers can cause the system to become unstable, especially in the presence of high-frequency noise.
Apply
Temperature control system: The power of the heater is adjusted by accumulating temperature errors to ensure that the final temperature is stable at the set value.
Flow control system: Adjust the opening of the valve by accumulating flow errors to ensure that the flow is stable at the set value.
Pressure control system: The output of the pump is adjusted by accumulating pressure errors to ensure that the pressure in the pipeline is stable at the set value.
Motor control system: By accumulating motor speed error to adjust the output of the motor to ensure that the motor speed is stable at the set value.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













