What is a Proportional Controller?
What is a Proportional Controller?
Proportional controller is one of the most basic control algorithms in automatic control systems, usually represented by the letter "P". The proportional controller controls the response of the system by adjusting the output signal to be proportional to the error signal.
Basic principle
The basic idea of the proportional controller is to reduce the system error by adjusting the output signal of the controller. Error is the difference between the expected value and the actual measurement.
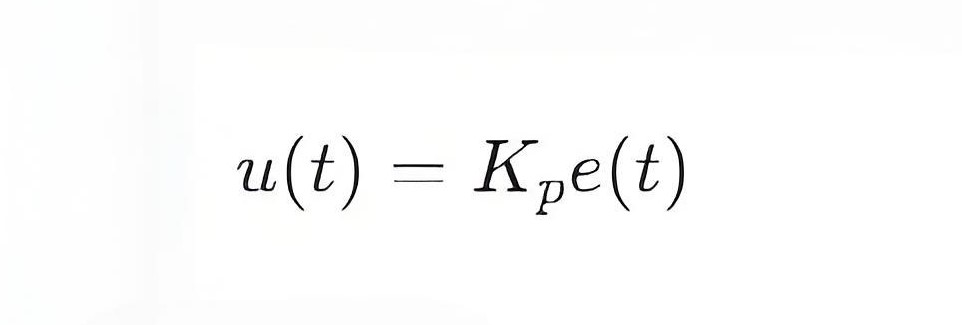
u(t) is the output signal of the controller.
Kp is Proportional Gain, which determines the magnification of the output signal to the error.
e(t) is the error signal, defined as e(t)=r(t)−y(t), where r(t) is the set value and y(t) is the actual measured value.
Advantage
Fast response: The proportional controller can quickly respond to changes in error.
Simple: simple structure, easy to understand and implement.
Flexibility: The response speed of the system can be flexibly adjusted by adjusting the proportional gain.
Shortcoming
Steady state error: Since the proportional controller only considers the current error, the system may have a certain steady state error.
Overshoot: If the proportional gain is not selected properly, it may cause the system to overshoot, that is, the output value oscillates near the set value.
Stability problems: Excessive proportional gain may cause system instability.
Apply
Temperature control system: Maintain the set temperature by adjusting the power of the heater.
Flow control system: Control the flow of fluid by adjusting the opening of the valve.
Pressure control system: Maintain the pressure in the pipeline by adjusting the output of the pump.
Motor control system: By adjusting the speed of the motor to achieve the required output power.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













