What is Transformation Ratio?
What is Transformation Ratio?
Transformer conversion ratio refers to the proportional relationship between the number of turns between the primary and secondary windings of the transformer, which determines the voltage conversion capability of the transformer. The conversion ratio is one of the most basic characteristics of a transformer and is used to describe how the transformer changes the input voltage to the output voltage.
Definition
The conversion ratio of the transformer is defined as the ratio of the number of turns in the primary winding N1 to the number of turns in the secondary winding N2:
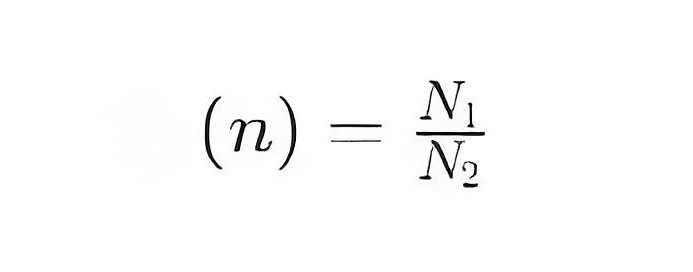
The conversion ratio can also be expressed in terms of voltage, that is, the ratio of primary voltage V1 to secondary voltage V2:
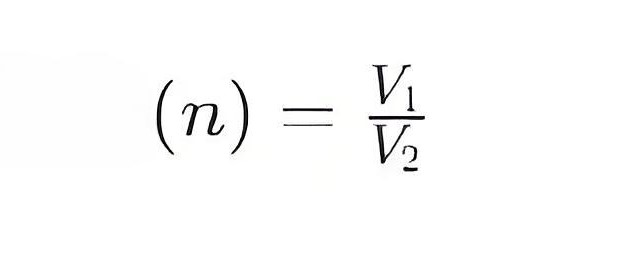
Type
Booster transformer: when N 1<N 2, the transformation ratio n<1, the primary voltage is lower than the secondary voltage, that is, V1<V2.
Step-down transformer: when N1>N2, the conversion ratio n>1, the primary voltage is higher than the secondary voltage, that is, V1>V2
Isolation transformer: when N1=N2, the transformation ratio n=1, the primary voltage is equal to the secondary voltage, that is V1 is equal to V2.
Working principle
The working principle of transformers is based on the law of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current passes through the primary winding, it creates an alternating magnetic field around the winding. This magnetic field passes through the secondary winding and induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the secondary winding according to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. The size of the induced electromotive force is proportional to the number of turns in the winding, so:
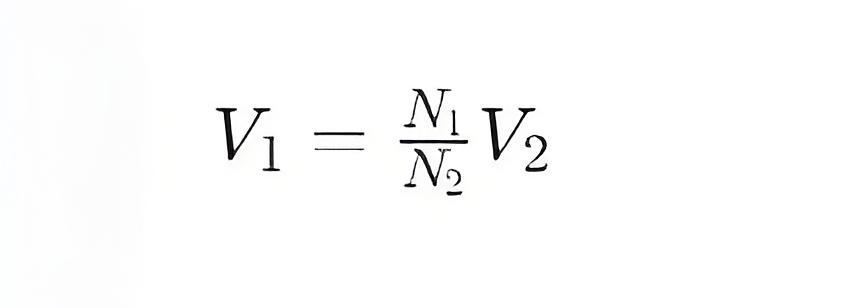
Current relation
In addition to voltage changes, transformers also change current. According to the law of electromagnetic induction, the primary current I1 and the secondary current I2
The relationship between them follows the following rules:
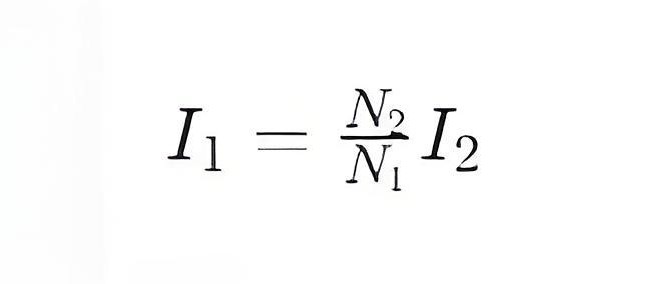
This means that if the transformer is a booster transformer, the secondary current will be reduced; If it is a step-down transformer, the secondary current will increase.
Power relation
Ideally, the input power of the transformer is equal to the output power (ignoring the loss) :
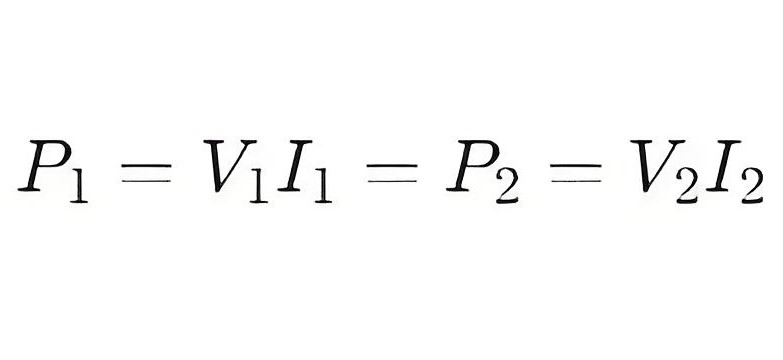
Application scenario
Transformer conversion ratio has a wide range of application scenarios, including but not limited to:
Power transmission: In the process of power transmission, booster transformers are used to increase voltage to reduce energy loss in the transmission line; Step-down transformers are used to convert high voltage electricity at the end user to low voltage electricity suitable for domestic and industrial use.
Power distribution: In a power distribution system, transformers are used to convert the voltage of a high-voltage grid into a voltage suitable for use on the local grid.
Industrial applications: In a variety of industrial equipment, transformers are used to convert the grid voltage to the voltage suitable for the operation of a particular equipment.
Laboratory and research: In laboratories, transformers are used to generate specific voltages or currents to meet experimental needs.
Design and selection
When designing and selecting a transformer, the following factors need to be considered:
Load requirements: Select the appropriate conversion ratio according to the specific requirements of the load to ensure that the output voltage meets the requirements of the load.
Voltage level: Select the corresponding transformer according to the voltage level of the power system.
Capacity: Select the capacity of the transformer according to the maximum power requirements of the load.
Efficiency: Choose an efficient transformer to reduce energy loss.
Reliability: Select high-quality transformers to ensure long-term stable operation.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













