How are core loss and hysteresis loss related?
Relationship Between Core Loss and Hysteresis Loss
Core loss (Core Loss) and hysteresis loss (Hysteresis Loss) are two common types of losses in electromagnetic devices. They are closely related but have distinct characteristics and mechanisms. Below is a detailed explanation of these two losses and their relationship:
Core Loss
Core loss refers to the total energy loss that occurs within the core material due to the magnetization process in an alternating magnetic field. Core loss primarily consists of two components: hysteresis loss and eddy current loss
Hysteresis Loss
Hysteresis loss is the energy loss due to the hysteresis phenomenon in the core material during the magnetization process. Hysteresis is the lagging of the magnetic induction B behind the magnetic field strength H. Each magnetization cycle consumes a certain amount of energy, which is dissipated as heat, forming the hysteresis loss.
Hysteresis loss can be expressed by the following formula:
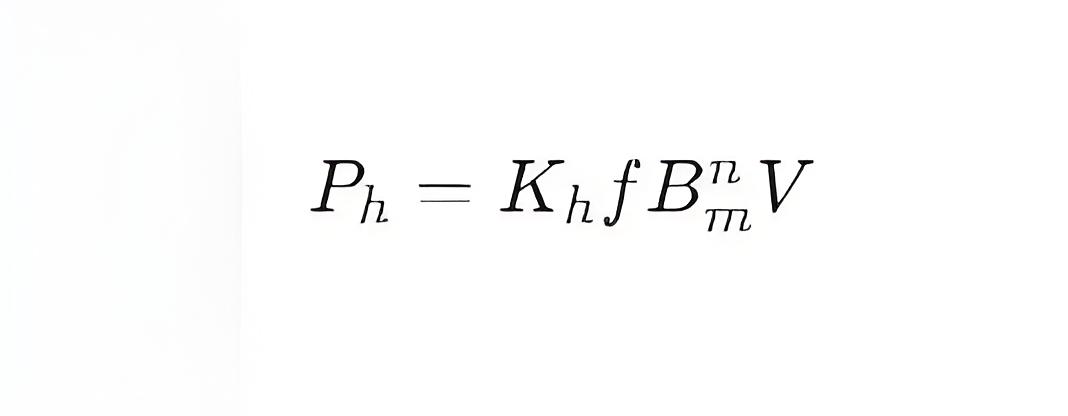
where:
Ph is the hysteresis loss (unit: watts, W)
Kh is a constant related to the material properties
f is the frequency (unit: hertz, Hz)
Bm is the maximum magnetic induction (unit: tesla, T)
n is the hysteresis exponent (typically between 1.2 and 2)
V is the volume of the core (unit: cubic meters, m³)
Eddy Current Loss
Eddy current loss is the energy loss due to eddy currents induced in the core material by the alternating magnetic field. These eddy currents flow within the material and generate joule heat, leading to energy loss. Eddy current loss is related to the resistivity of the core material, the frequency, and the magnetic induction.
Eddy current loss can be expressed by the following formula:
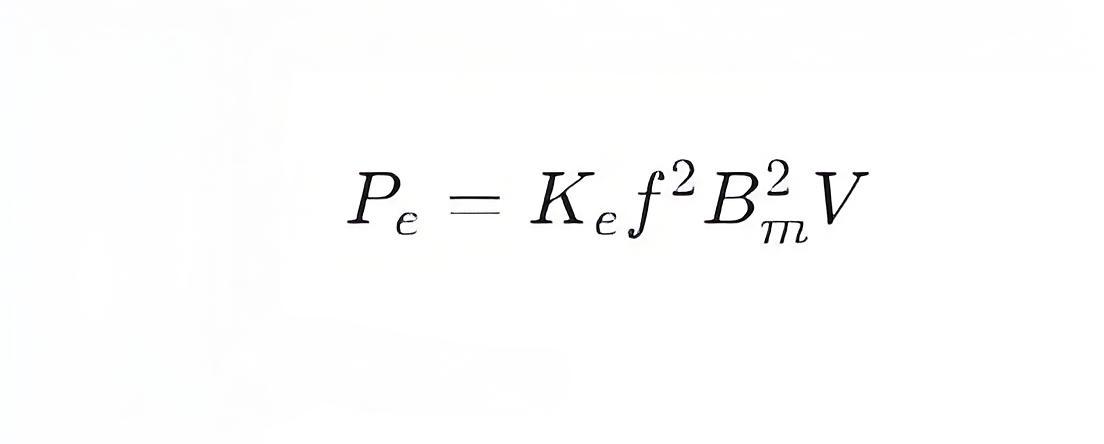
where:
Pe is the eddy current loss (unit: watts, W)
Ke is a constant related to the material properties
f is the frequency (unit: hertz, Hz)
Bm is the maximum magnetic induction (unit: tesla, T)
V is the volume of the core (unit: cubic meters, m³)
Relationship
Common Factors:
Frequency
f: Both core loss and hysteresis loss are proportional to the frequency. Higher frequency results in more magnetization cycles within the core, leading to higher losses.
Maximum Magnetic Induction
Bm : Both core loss and hysteresis loss are related to the maximum magnetic induction. Higher magnetic induction results in more intense magnetic field variations, leading to higher losses.
Core Volume
V: Both core loss and hysteresis loss are proportional to the volume of the core. Larger volumes result in greater total losses.
Different Mechanisms:
Hysteresis Loss: Primarily caused by the hysteresis phenomenon in the core material, which is related to the magnetization history of the material.
Eddy Current Loss: Primarily caused by eddy currents induced in the core material by the alternating magnetic field, which are related to the resistivity of the material and the magnetic field strength.
Summary
Core loss is composed of hysteresis loss and eddy current loss. Hysteresis loss is mainly related to the magnetization characteristics of the core material, while eddy current loss is mainly related to the eddy currents induced by the alternating magnetic field. Both are influenced by frequency, magnetic induction, and core volume, but they have distinct physical mechanisms. Understanding the nature and relationship of these losses is crucial for optimizing the design of electromagnetic devices and improving their efficiency.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













