What effect does a lower power factor have on effective power (kilowatts)?
Power factor is an index to measure the relationship between the actual effective power consumed in an AC circuit and the apparent power. The effect of low power factor on effective power mainly has the following points:
Effective power reduction
The power factor is defined as the ratio of effective power (kW) to apparent power (kVA) :
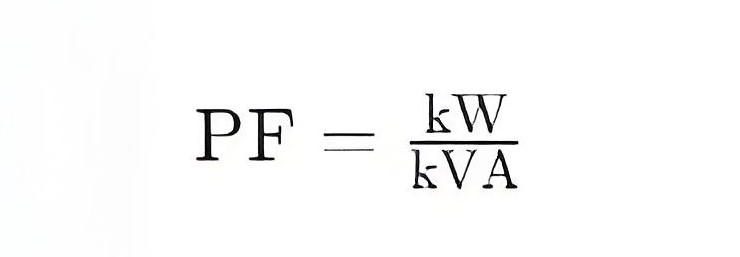
If the power factor is low, it means that for the same amount of apparent power, less effective power is actually used to do work. In other words, a portion of the energy in the system is used to flow back and forth between inductive or capacitive components, rather than being converted into useful mechanical or thermal energy.
For example, if a circuit has a power factor of 0.8, then out of 1000 kVA's apparent power, only 800 kW is effective power. The remaining 200 kVA represents Reactive Power (kVAR), which does not actually do any work.
Energy waste
Since a lower power factor means that more energy is used for reactive power exchange rather than for actual work, energy is wasted. Although this part of the energy is not directly converted into useful work, it still generates heat through the components in the circuit, thus increasing the energy consumption.
Equipment utilization decline
When the power factor is low, the power equipment (such as generators, transformers, cables, etc.) needs to carry more current to transmit the same amount of effective power. This means that the actual utilization of devices decreases because they need to carry more apparent power to reach the desired effective power level.
Increase in grid burden
A low power factor can lead to an increased burden on the grid because the grid needs to deliver more current to provide the same effective power. This not only increases the load on the grid, but also may lead to increased voltage drop and line loss, affecting the quality and efficiency of the power supply.
Tariff increase
For electricity users, the power company usually charges the electricity bill based on the user's apparent power. If the power factor is low, even if the actual effective power used is unchanged, the user's electricity bill may increase accordingly due to the increase in apparent power. In addition, some electricity providers will impose additional charges on customers whose power factor is below a certain standard.
Ways to improve power factor
In order to improve the power factor and reduce the above negative effects, the following measures can be taken:
Use compensation capacitors: Adding compensation capacitors to the circuit can offset part of the inductive load and improve the power factor.
Load optimization: Minimize the proportion of nonlinear and inductive loads, or combine them with capacitive loads.
Use energy-saving equipment: Choose energy-efficient equipment to reduce the consumption of ineffective energy.
Reasonable load arrangement: reasonable planning of the working time of electrical equipment to avoid unnecessary energy consumption.
By improving the power factor, you can increase the efficiency of the system, reduce energy waste, and reduce the cost of electricity.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













