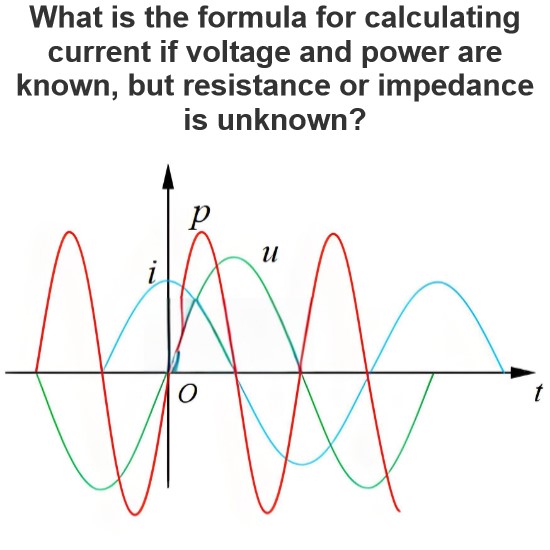
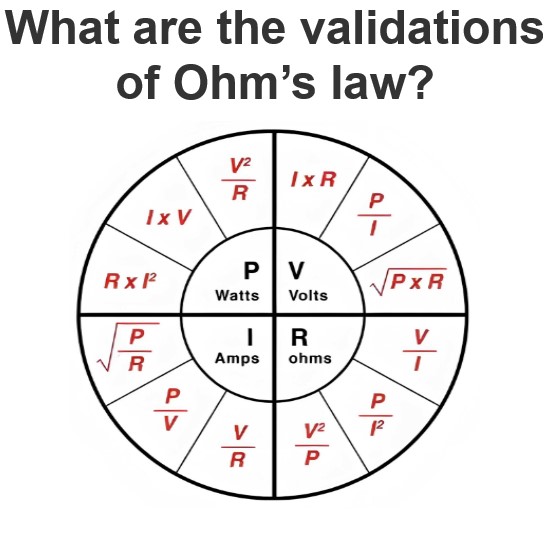
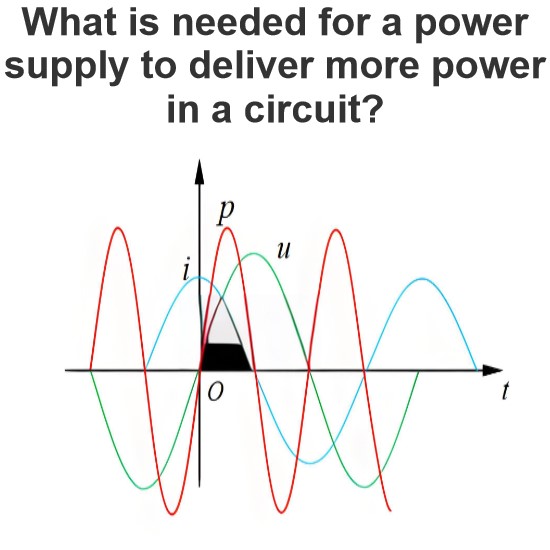
What is a Coulomb's Law?
What is a Coulomb's Law?
Coulomb’s Law Definition
Coulomb’s law defines the force between two stationary, electrically charged particles, known as the electrostatic force.
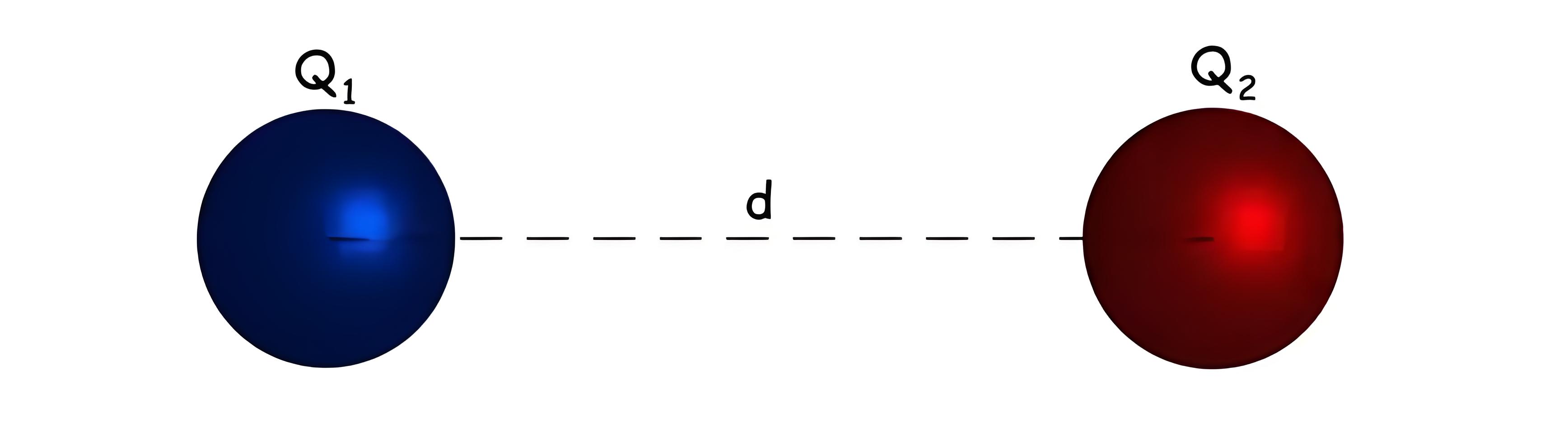
Electrostatic Force
The electrostatic force is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Coulomb’s Law Formula
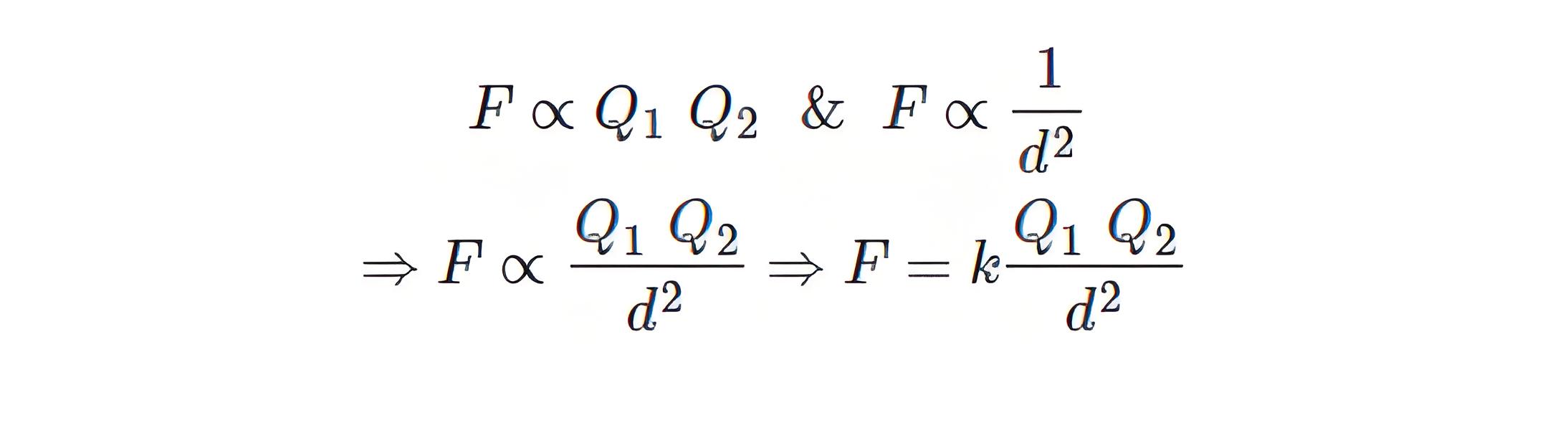
Coulomb’s Constant
Coulomb’s constant (k) in a vacuum is approximately 8.99 x 10⁹ N m²/C², and it varies with the medium.
Historical Background
Charles-Augustin de Coulomb formalized Coulomb’s law in 1785, building on earlier observations by Thales of Miletus.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.