What is short-circuit Current?
What is short-circuit Current?
Short circuit current definition
Short-circuit current is the current flowing through the power system when an abnormal connection occurs between phase and phase or between phase and ground (or neutral line) during operation. The value can be much greater than the rated current and depends on the electrical distance between the short circuit point and the power supply.
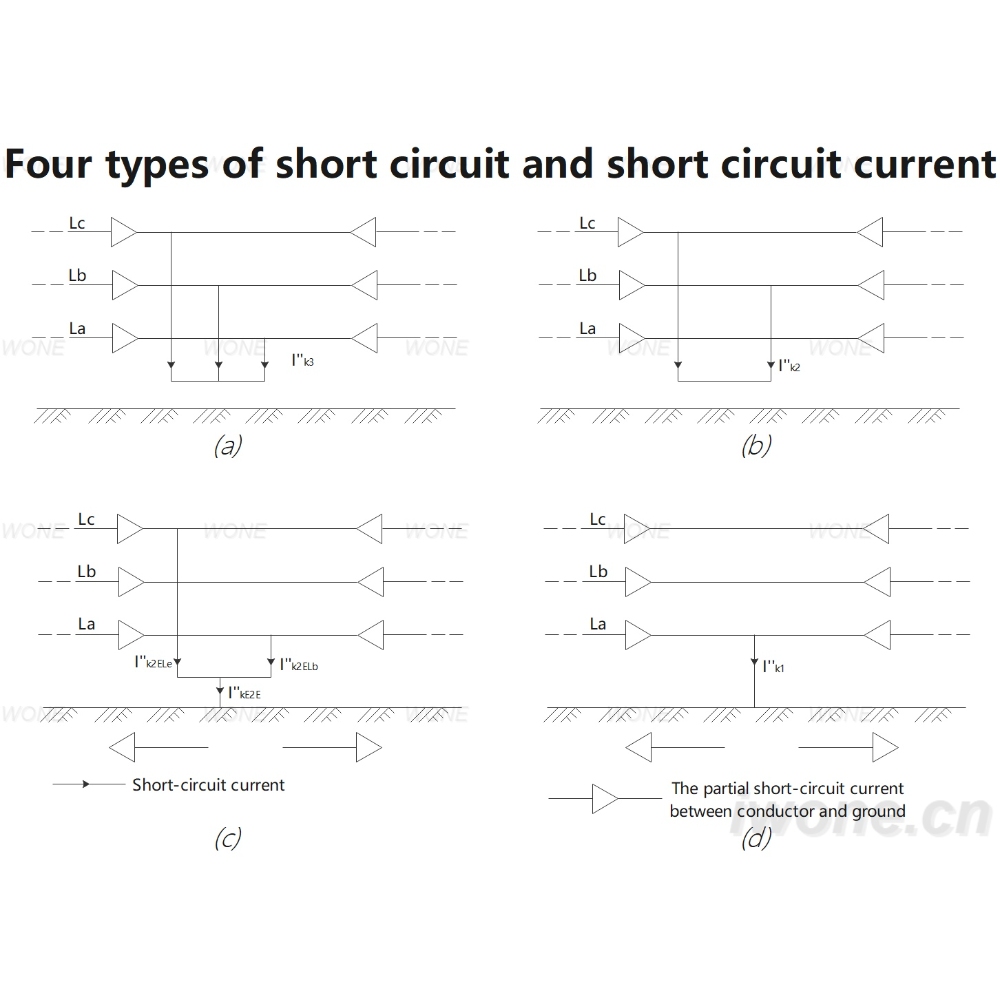
Type of short circuit
Three-phase short circuit
Two-phase short circuit
Single to ground short circuit
Short circuit in both directions
Purpose of calculation
In order to limit the harm of short circuit and reduce the influence range of fault.
Short-circuit calculation scenario
When selecting electrical equipment and current-carrying conductors, the thermal and dynamic stability must be checked by short-circuit current.
Select and set the relay protection device so that it can correctly cut out the short circuit fault.
Determine the reasonable main wiring scheme, operation mode and current limiting measures.
Protect the electrical equipment of the power system from damage in the most serious short-circuit state, and minimize the harm caused by short-circuit failure
Calculation condition
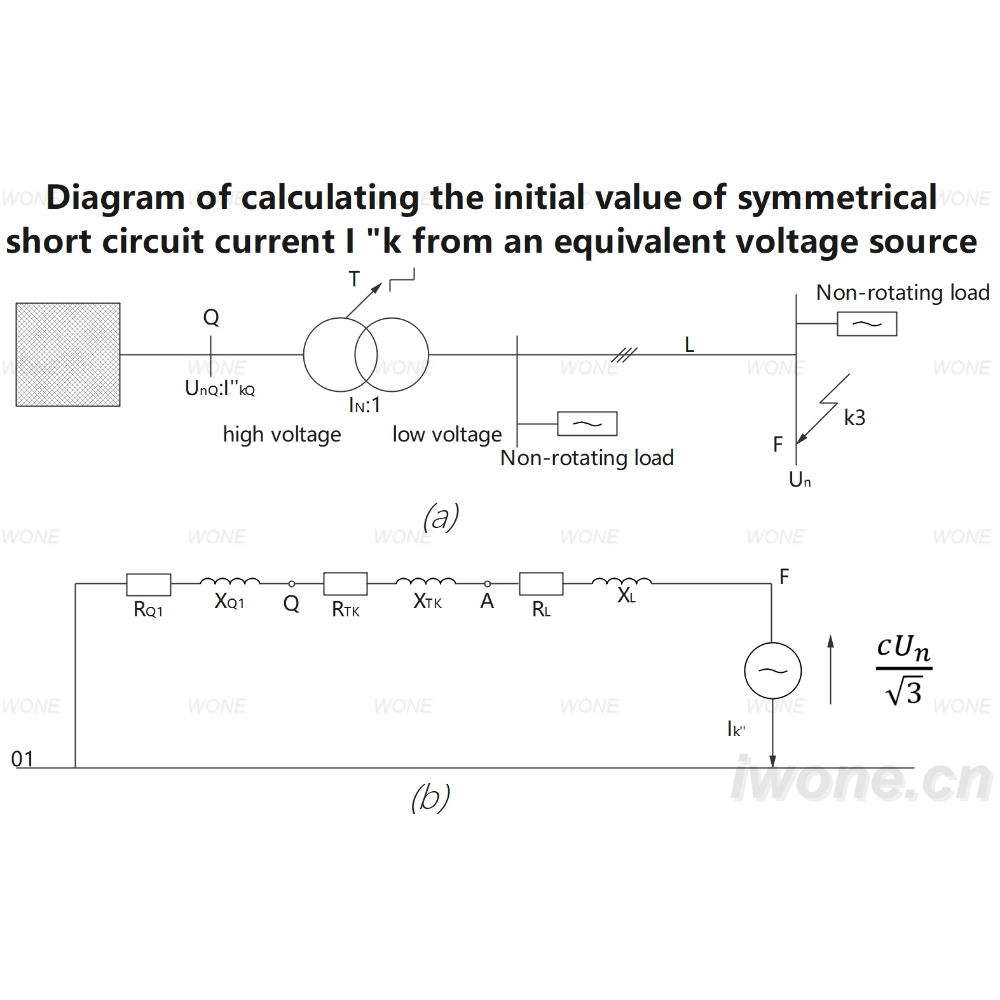
Assume that the system has an infinite capacity. The bus voltage of the system can be maintained after the short circuit at the user. That is, the calculated impedance is much larger than the system impedance
When calculating the short circuit current in the high voltage appliance, only the reactance of the generator, transformer and reactor should be considered, while the resistance should be ignored. For overhead lines and cables, only when the resistance is greater than 1/3 reactance, the resistance needs to be counted, and the reactance is generally only counted and the resistance is ignored.
Short-circuit current calculation formula or calculation chart, are based on three-phase short-circuit calculation conditions. Because the short-circuit current of single-phase short-circuit or two-phase short-circuit is less than the three-phase short-circuit current. An appliance that can break the three-phase short-circuit current must be able to break the single-phase short-circuit current or the two-phase short-circuit current.
Major Parameter
Sd : three-phase short circuit capacity (MVA), short circuit capacity check switch breaking capacity.
Id : Effective value of three-phase short-circuit current cycle component, short circuit current check switch breaking current and thermal stability.
Ic : three-phase short circuit first cycle full current RMS, referred to as impulse current RMS check dynamic stability.
ic : three-phase short circuit first cycle full current peak, referred to as impulse current peak check dynamic stability.
x : Reactance (Ω)
Per unit value
A reference capacity (Sjz) and a reference voltage (Ujz) are selected for calculation. Each parameter in the short-circuit calculation is converted into the ratio of the reference quantity of the parameter (relative to the reference quantity), which is called per unit value.
Per unit calculation
Per unit capacity : S*=S/Sjz
Per unit voltage : U*=U/Ujz
Current per unit value : I*=I/Ijz
Formula for calculating three-phase short-circuit current of infinite capacity system
Per unit of short circuit current : Id*=1/x* (reciprocal of total reactance standard value)
Effective short circuit current : Id=Ijz*I*d=Ijz/x*(KA).
Effective impact current value : Ic=Id*√1+2(KC-1) 2(KA), where KC impact coefficient is 1.8, so Ic=1.52Id
Peak impulse current : ic=1.41*Id*KC=2.55Id(KA)
Preventive measures
Select and verify the electrical equipment correctly. The rated voltage of the electrical equipment should be consistent with the rated voltage of the line
The setting value of the relay protection and the rated current of the melt are correctly selected, and the quick-break protection device is adopted
Install lightning arresters in substations, and install lightning arresters around transformers and on lines to reduce lightning damage
Ensure overhead line construction quality and strengthen line maintenance
Ensure overhead line construction quality and strengthen line maintenance
Strengthen management to prevent small animals from entering the power distribution room and climbing on the electrical equipment
Remove conductive dust in time to prevent it from entering the electrical equipment
Set a marker where the cable is buried
The operation and maintenance personnel of the power system should carefully study the procedures, strictly abide by the rules and regulations, and correctly operate the electrical equipment
We aim to gather electrical knowledge and share it with others.