What is Diversity Factor?
What is Diversity Factor?
Diversity Factor Definition
Diversity factor is defined as the ratio of the sum of maximum demands of individual loads to the simultaneous maximum demand of the system.
Importance of Diversity Factor
A high diversity factor means that a smaller electrical source can serve more loads, making it commercially viable.
Peak Load Timing
Different types of loads (domestic, commercial, industrial, etc.) have peak demands at different times, which helps in managing the overall load on the system.
Application in Electrical Systems
Understanding and applying the diversity factor helps in designing efficient and cost-effective electrical systems.
Calculation Example
For a power transformer with industrial, domestic, and municipal loads, the diversity factor is calculated based on their maximum demands and the transformer’s maximum demand.
Let us name an electrical substation as X. A, B, C and E are downstream substations connected to the substation X. The maximum demand of these substations is A megawatts, B megawatts, C megawatts D megawatt, and E megawatt respectively. The simultaneous maximum demand of the X substation is X megawatt. The diversity factor substitution would be
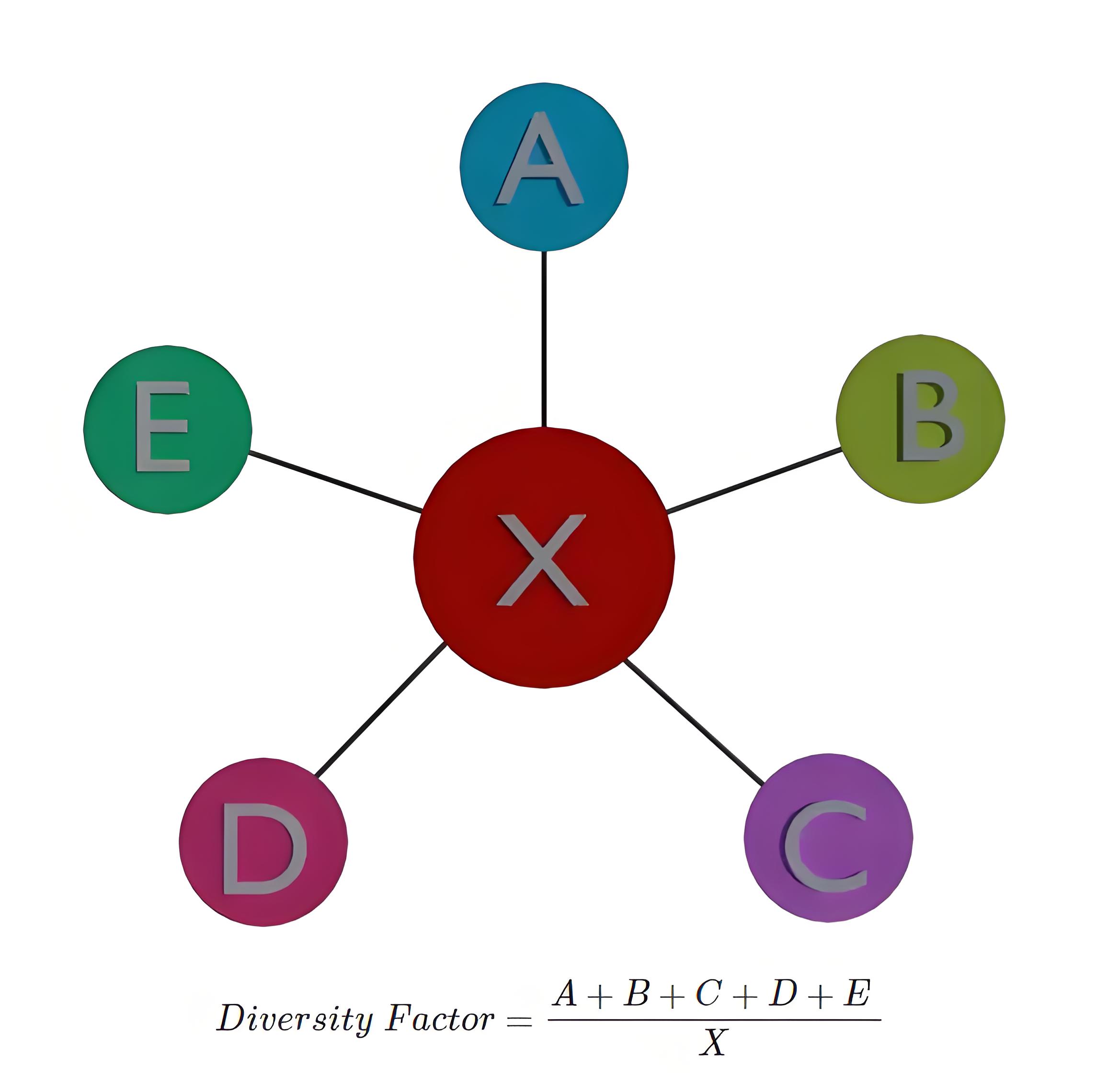
The diversity factor must always be greater than one. A higher diversity factor is desirable as it makes the electricity utility business more commercially viable.
Now you are going to show you one practical example of diversity factor. A power transformer is connected to the following loads. The industrial load is 1500 kW, the domestic load is 100 kW and the municipal load is 50 kW. The maximum demand for the power transformer is 1000 kW. The diversity factor of the transformer would be
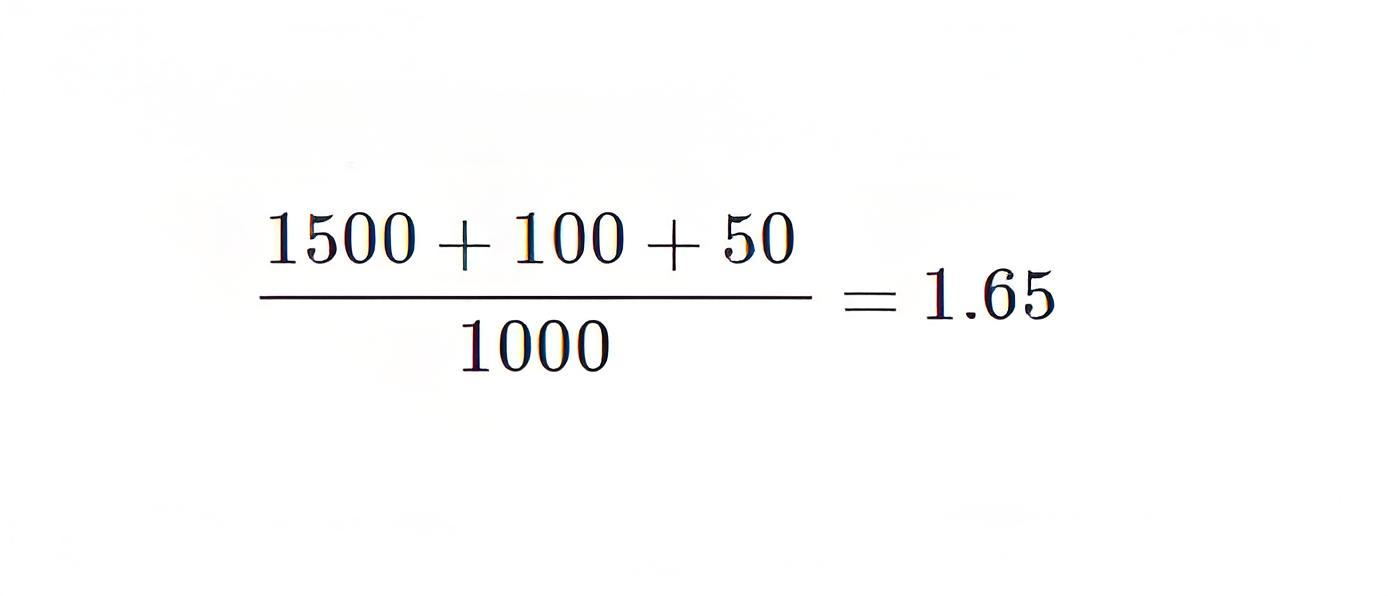
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.