Direct Current: What is it?
What is DC Current?
DC stands for Direct Current, although it is often called “DC Current”. DC current is defined as a unidirectional flow of electric charge. In DC current, the electrons move from an area of negative charge to an area of positive charge without changing direction. This is unlike alternating current (AC) circuits, where current can flow in both directions.
DC current can flow through conducting material like wire and also flow through the semiconductors.
The battery is a good example of a DC source. In a battery, the electrical energy is produced from the chemical energy stored in the battery. When a battery is connected to a circuit, it provides a constant flow of charge from the negative terminal to the positive terminal of the battery.
A rectifier is used to convert alternating current to direct current. And the inverter is used to convert direct current to alternating current.
DC Current Symbol
The DC current is a constant current. Therefore, the symbol of DC current is a straight line. The symbol of DC and AC current is as shown in the figure below.
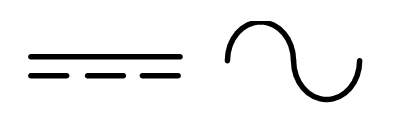
Symbol of DC and AC Current
Difference between AC and DC Current
Electrical energy is available in the form of Alternating current (AC) or Direct current (DC). In alternating current, the current reverses direction 50-60 times in a second depending on the frequency.
The main differences between AC and DC have been summarized in the below table;
Alternating Current (AC) |
Direct Current (DC) |
|
The direction of flow of current |
When an alternating current flowing through a circuit, it reverses its direction. |
When an alternating current flows through a circuit, it reverses its direction. |
Frequency |
The frequency of alternating current decides how many times it reverses its direction. If the frequency is 50 Hz, it means the current changes direction 50 times. |
Electrons keep changing its direction from forward to backward. |
Movement of Electron |
The magnitude of the instantaneous current varies with time. |
Electrons move only in a forward direction. |
Current magnitude |
The magnitude of the instantaneous current is varying with time. |
The magnitude is constant at each instant of time for pure DC. But it is variable for pulsating DC. |
Ranges between 0 and 1. |
Always equal to 1. |
|
Passive Parameter |
Impedance (Combination of Reactance and Resistance). |
It can connect with the resistive, inductive, and capacitive types of load. |
Types |
Sinusoidal, Trapezoidal, Square, Triangular |
Pure DC and Pulsating DC |
Transmission of electrical energy |
In a power system, the conventional method to transmit power is the HVAC transmission system. The losses are less but more than the HVDC transmission system. |
In a power system, the most emerging technology for transmission systems is the HVDC Transmission system. The losses are very less in the HVDC transmission system. |
Convert |
It can convert from an AC supply with the help of a rectifier. |
Cell phones, electric vehicles, electroplating, flashlights, etc. |
Type of load |
It can connect with the resistive, inductive, and capacitive types of load. |
It can connect only with the resistive type of load. |
Source |
AC Generator |
DC Generator and battery |
Dangerous |
It is dangerous. |
But it is more dangerous than AC for the same power rating. |
Application |
Most of the household, industrial and commercial equipment operates on DC. |
Cell phones, Electric vehicles, Electroplating, flashlights, etc. |
Table comparing Direct Current To Alternating Current
What Uses DC Current?
The DC current can easily get from the battery and solar cells. Most of the power electronics circuits require a DC supply. The application of DC current in various fields are listed below:
DC supply is used in many low voltage applications like charging mobile batteries. In domestic and commercial buildings, DC is used for emergency lighting, security camera, TV, etc.
In a vehicle, the battery is used to start the engine, lights, and ignition system. The electric vehicle runs on a battery (DC current).
In communication, a 48V DC supply is used. Generally, it uses a single wire for communication and uses a ground for the return path. Most of the communication networking devices operate on the DC current.
High-voltage Power Transmission is possible with the HVDC Transmission line. There are many advantages of the HVDC Transmission system over the conventional HVAC Transmission system. An HVDC system is more efficient than an HVAC system, as it does not experience power losses due to the corona effect or skin effect.
In a solar power plant, energy is generated in the form of DC current.
The AC power cannot be stored like DC. So, to store electrical energy, DC is always used.
In a traction system, the locomotive engines are run on DC current. In diesel locomotives also, the fan, lights, AC, and sockets operate on DC current.
How To Measure DC Current
The DC current can be measured by a multimeter. The multimeter is connected in series with the load.
The Black (COM) probe of a multimeter is connected to the negative terminal of the battery. The positive probe (red probe) is connected to the load. The positive terminal of the battery is connected to the load. The connection diagram is shown in the figure below:
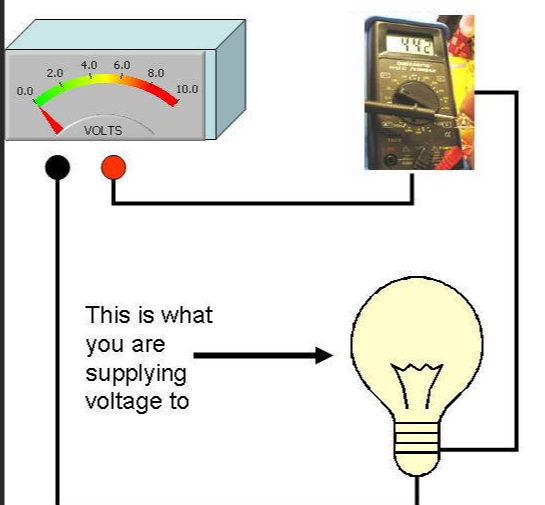
Set the type of current DC in a multimeter. The reading shows the value of DC current flowing the load. The clamp-on meter is also used to measure the DC current flowing through a conductor.
Which Way Does DC Current Flow?
Current is a flow of charge or electrons. The direction of the current depends on the direction of the flow of charge.
The electrons flow from the negative end of the battery to the positive end of the battery. Then the current indicates directions in the direction from the positive to the negative end.
Benjamin Franklin observed that something moving through the conductor. But at that time, protons and electrons are not discovered. So, he does not know what is moving through the conductor.
He assumed that current flow from the higher concentration region to the lower concentration region. And he called a higher concentration region positive and a lower concentration region as negative. Therefore, the current flows from positive to negative. And this direction is known as the conventional direction of the flow of current.
After the invention of electrons and protons, it is confirmed that current moves from the negative to the positive end of the battery. But still, we are assuming the direction of current as of the conventional method.
Who Invented DC Current?
The DC was first introduced by Italian physicist Alessandro Volta’s battery. At that time direction of the current was not introduced. French physicist Ampere gives an opinion that current travel in one direction from positive to negative.
In the late 19th century, three inventors, Nikola Tesla, George Westinghouse, and Thomas Edison combat choosing the electricity system.
The company of Edison promoted the DC system as the dominant electric system and it is better than the AC system. He built the first power plant and started to transmit DC power to a home in New York.
The competition began between Edison and Tesla. Because tesla supports the AC system and it can transmit the AC power over a long distance. After this war, Westinghouse made the first hydroelectric generator placed on Niagara Falls. And the winner of the current war. From now, the AC system will be dominant over the DC system.
But nowadays, due to more power electronics equipment, DC current is used to power low-voltage power electronics devices.
Source: Electrical4u
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
Electrical4U is dedicated to the teaching and sharing of all things related to electrical and electronics engineering.