How to Wire Solar Panel & Batteries in Parallel for 12V System
12V Solar Panel and Battery Parallel Wiring for Power Systems
A 12V connection is the most prevalent setup for wiring solar panels to batteries. Typically, to convert this 12VDC power into a 120/230VAC system suitable for common household use, both the photovoltaic (PV) panels and batteries are connected in parallel. This configuration enables efficient power generation, battery charging, and powering of AC loads, as well as directly operating DC - powered appliances. Let's explore the step - by - step process of wiring two or more solar panels and batteries in parallel, integrating them with a solar charge controller and an automatic inverter or uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to meet diverse power needs.
Most solar panels and batteries are available in voltage ratings such as 12V, 24V, 36V, etc. When you aim to increase the capacity of your solar power system, a parallel wiring configuration becomes essential. For instance, if a single battery can power a ceiling fan for 6 hours, connecting two batteries of the same capacity in parallel can extend the fan's operating time to approximately 12 hours—nearly double the duration. Moreover, two parallel - connected solar panels not only charge the batteries more rapidly but also provide additional power to support a greater number of electrical loads.
This parallel wiring approach is particularly crucial for 12V systems, which include components like a 12V charge controller and inverter. That's why, in a 12V setup, it's common practice to connect multiple 12VDC solar panels and batteries in parallel.
It's important to note that depending on specific requirements, multiple solar panels and batteries can also be wired in series, parallel, or a combination of series - parallel configurations for DC systems with different voltage levels, such as 12V, 24V, 36V, or 48V.
In a parallel connection, an important electrical principle applies: the voltage remains constant across all connected components, while the current values add up. For example, when two solar panels or batteries, each rated at 12VDC, 120W, and 10A, are connected in parallel
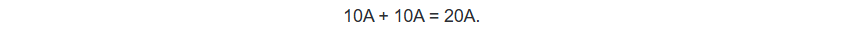
Same is the case for batteries, i.e. we can increase the ampere hour (Ah) capacity of batteries when connected in parallel.

While the voltage level of battery as well as solar panel remains same (Parallel connection)
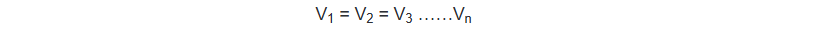
That is, the voltage remains 12V for both the 12V solar panels and batteries.
Important Note: When connecting batteries in series or parallel, it is crucial that all batteries have the same ampere - hour (Ah) capacity, just as solar panels in the same configuration should have the same voltage level. In this parallel setup, while the voltage from both the batteries and PV panels stays at 12V, the overall amperage capacity increases. This allows for seamless integration of the power - generating PV panels and energy - storing batteries (which serve as backup power) with a 12V UPS/inverter and a solar charge controller.
During daylight hours with normal sunshine, the DC - to - AC inverter is powered directly by the solar panels. In situations like shading or at night, the inverter draws power from the batteries. The inverter then converts the 12VDC input into either 120VAC (in the US) or 230VAC (in the UK and EU), depending on the local AC voltage standards, and supplies power to AC loads such as light bulbs and fans. Additionally, DC - operated devices can be directly connected to the charge controller's DC load terminals.
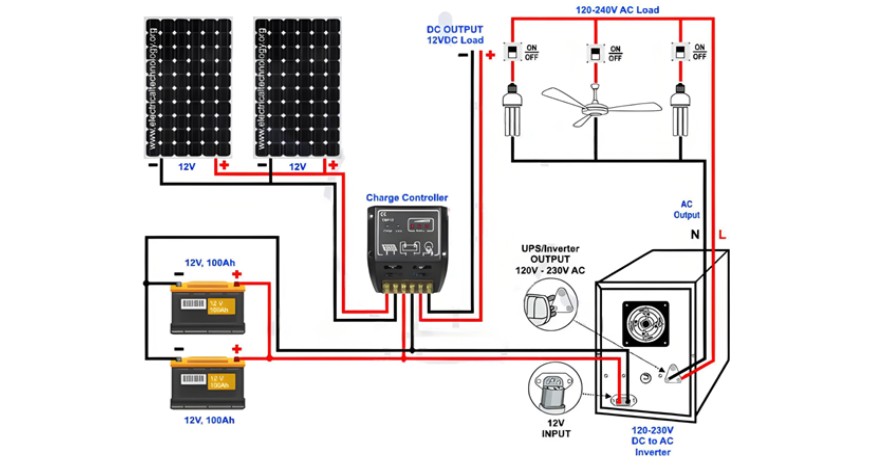
Wiring two or more solar panels and batteries in parallel is straightforward. As illustrated in the figure below, simply connect the positive terminal of one solar panel or battery to the positive terminal of another, and do the same for the negative terminals.
The accompanying wiring diagram demonstrates how two 12V, 10A, 120W solar panels connected in parallel can charge two 12V, 100Ah batteries also connected in parallel. During the day with normal sunlight, this setup can also power AC loads through the batteries and the inverter. When shading occurs or at night, when the solar panels are unable to generate power, the stored energy in the batteries acts as backup power. The batteries then supply electricity to the AC loads via the inverter. This entire operation is managed automatically by the UPS, eliminating the need for manual intervention, changeover switches, or automatic transfer switches (ATS) to turn electrical appliances and breakers on or off, ensuring a hassle - free power supply experience.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.